重要研究成果
羅佩凌 博士
(2023)
Communications Chemistry, 6, 130 (2023)
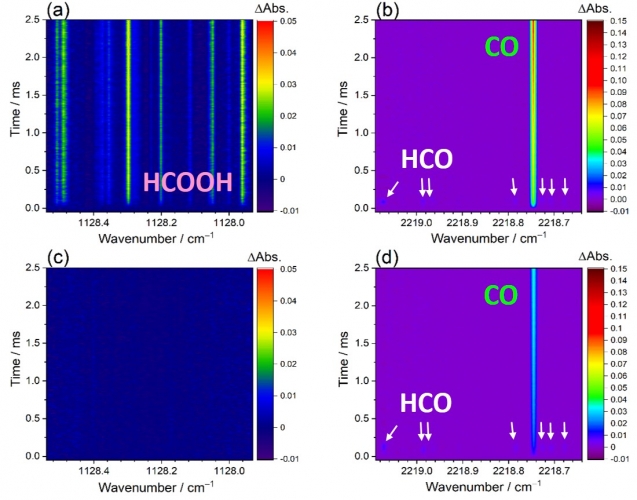
Ozonolysis of isoprene is considered to be an important source of formic acid (HCOOH), but its underlying reaction mechanisms related to HCOOH formation are poorly understood. Here, we report the kinetic and product studies of the reaction between the simplest Criegee intermediate (CH2OO) and formaldehyde (HCHO), both of which are the primary products formed in ozonolysis of isoprene. By utilizing time-resolved infrared laser spectrometry with the multifunctional dual-comb spectrometers, the rate coefficient kCH2OO+HCHO is determined to be (4.11 ± 0.25) × 10−12 cm3 molecule−1 s−1 at 296 K and a negative temperature dependence of the rate coefficient is observed and described by an Arrhenius expression with an activation energy of (–1.81 ± 0.04) kcal mol−1. Moreover, the branching ratios of the reaction products HCOOH + HCHO and CO + H2O + HCHO are explored. The yield of HCOOH is obtained to be 37–54% over the pressure (15–60 Torr) and temperature (283–313 K) ranges. The atmospheric implications of the reaction CH2OO + HCHO are also evaluated by incorporating these results into a global chemistry-transport model. In the upper troposphere, the percent loss of CH2OO by HCHO is found by up to 6% which can subsequently increase HCOOH mixing ratios by up to 2% during December-January-February months.
賴品光 博士
(2023)
Advanced Materials. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202208966 (2023).
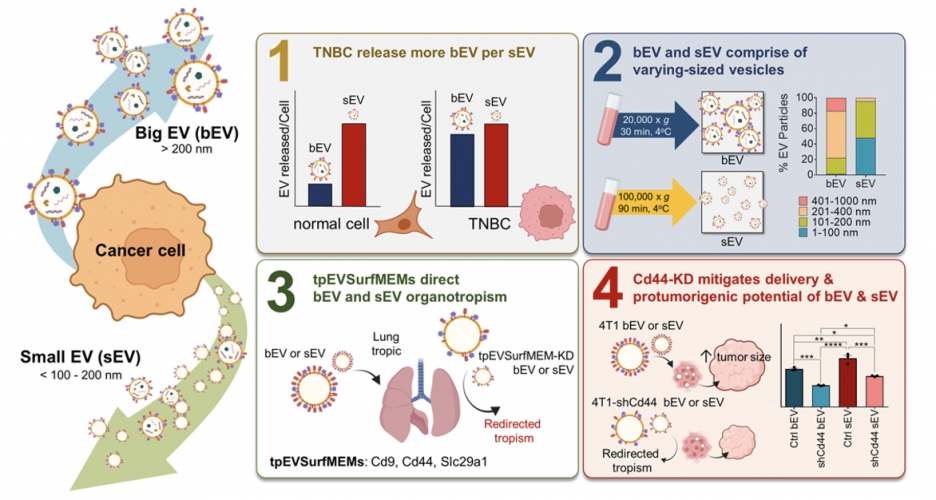
Our latest publication employed PalmGRET, a bioluminescence-resonance-energy-transfer (BRET)-based EV reporter, to discover an abundant release of big EVs (bEVs; >200 nm) by aggressive breast cancers when compared to epithelial and less malignant cells. bEVs have been largely overshadowed by small EVs (sEVs; <200 nm) in EV research in the past decades. This is the first study to accurately detect and systematically compare biophysical property and in vivo profiles of breast cancer bEVs and sEVs. This is followed by the identification of EV surface oncoproteins, and their role in modulating organotropism and tumorigenic potential of the bEVs and sEVs. Our landmark findings impart a broad and deep reference for upcoming EV studies, with an emphasis on EV engineering for diagnosis and therapeutic applications.
目前位置:關於本所 / 重要研究成果 / 第 4 頁
中央研究院 原子與分子科學研究所版權所有 |
個人隱私權聲明 |
保有個資檔案公開項目彙整表 |
行動版
地址: 106319 台北市羅斯福路四段一號 或 106923 臺北臺大郵局 第23-166號信箱
電話:886-2-2362-0212 傳真:886-2-2362-0200 電子郵件:iamspublic@gate.sinica.edu.tw
最後更新於 2025-05-09 13:50:00
地址: 106319 台北市羅斯福路四段一號 或 106923 臺北臺大郵局 第23-166號信箱
電話:886-2-2362-0212 傳真:886-2-2362-0200 電子郵件:iamspublic@gate.sinica.edu.tw
最後更新於 2025-05-09 13:50:00
 中央研究院 原子與分子科學研究所
中央研究院 原子與分子科學研究所
