eLife 9, e53580 (2020).
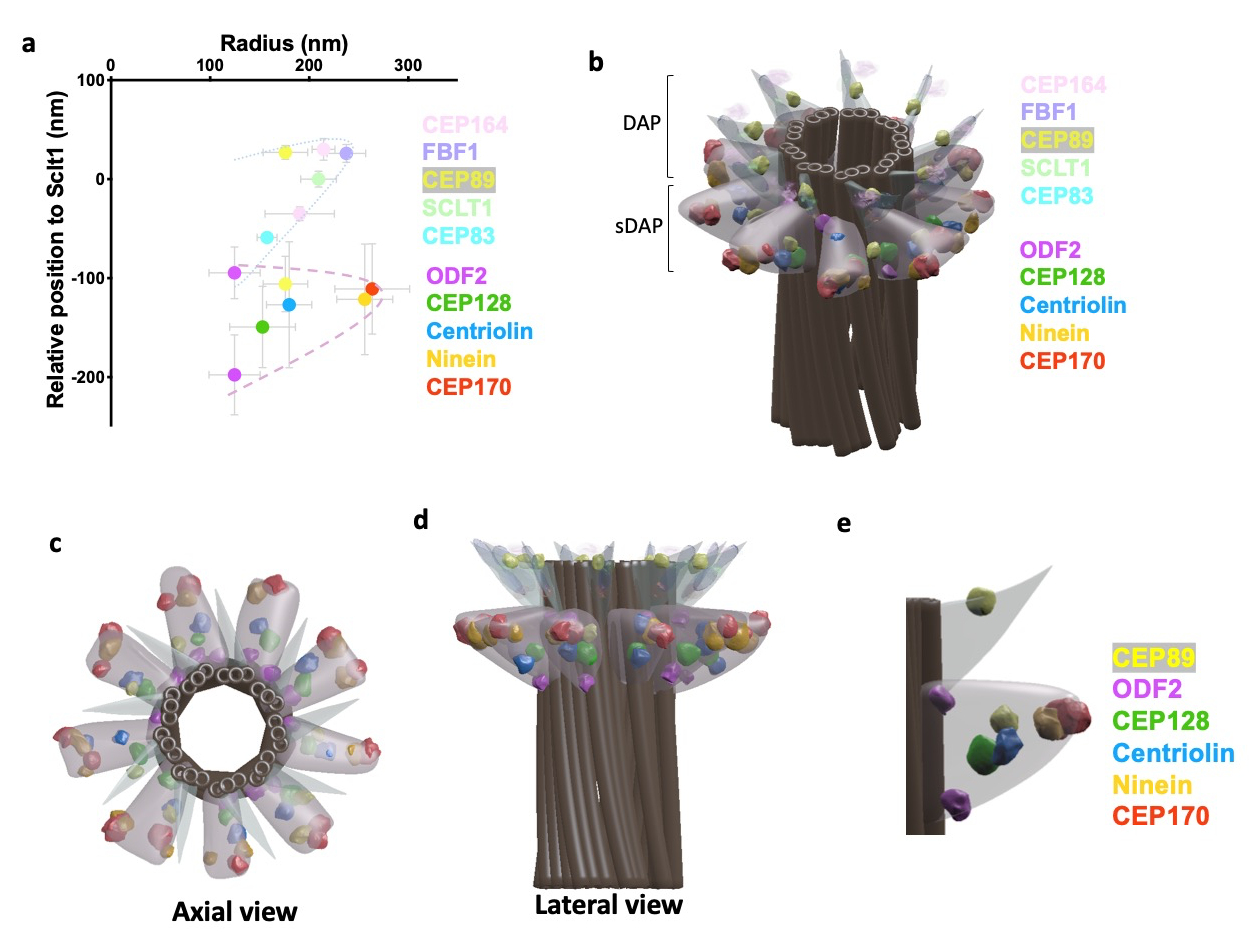
Subdistal appendages (sDAPs) are centriolar elements observed proximal to the distal appendages (DAPs) in vertebrates. Despite their obvious presence, structural and functional understanding of sDAPs remains elusive. Here, by combining super-resolved localization analysis and CRISPR-Cas9 genetic perturbation, we find that, although DAPs and sDAPs are primarily responsible for distinct functions in ciliogenesis and microtubule anchoring respectively, the presence of one element actually affects the positioning of the other. Specifically, we find dual layers of both ODF2 and CEP89, where their localizations are differentially regulated by DAP and sDAP integrity. DAP depletion relaxes longitudinal occupancy of sDAP protein ninein to cover the DAP region, implying a role of DAPs in sDAP positioning. Removing sDAPs alter the distal border of centrosomal γ-tubulins, illustrating a new role of sDAPs. Together, our results provide an architectural framework of sDAPs to shed light on functional understanding, surprisingly revealing the coupling between DAPs and sDAPs.
T. Tony Yang, Weng Man Chong, Won-Jing Wang, Gregory Mazo, Barbara Tanos, Zhengmin Chen, Thi Minh Nguyet Tran, Yi-De Chen, Rueyhung Roc Weng, Chia-En Huang, Wann-Neng Jane, Meng-Fu Bryan Tsou* & Jung-Chi Liao*
Nature Communications, 9, 2023 (2018).
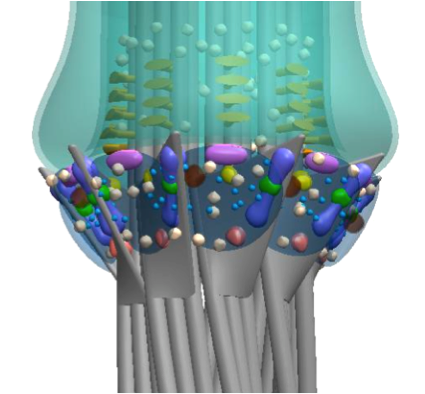
Distal appendages (DAPs) are nanoscale, pinwheel-like structures protruding from the distal end of the centriole that mediate membrane docking during ciliogenesis, marking the cilia base around the ciliary gate. Here we determine a super-resolved multiplex of 16 centriole-distal-end components. Surprisingly, rather than pinwheels, intact DAPs exhibit a cone-shaped architecture with components filling the space between each pinwheel blade, a new structural element we term the distal appendage matrix (DAM). Specifically, CEP83, CEP89, SCLT1, and CEP164 form the backbone of pinwheel blades, with CEP83 confined at the root and CEP164 extending to the tip near the membrane-docking site. By contrast, FBF1 marks the distal end of the DAM near the ciliary membrane. Strikingly, unlike CEP164, which is essential for ciliogenesis, FBF1 is required for ciliary gating of transmembrane proteins, revealing DAPs as an essential component of the ciliary gate. Our findings redefine both the structure and function of DAPs.
Scientific Reports 5, 14096 (2015).
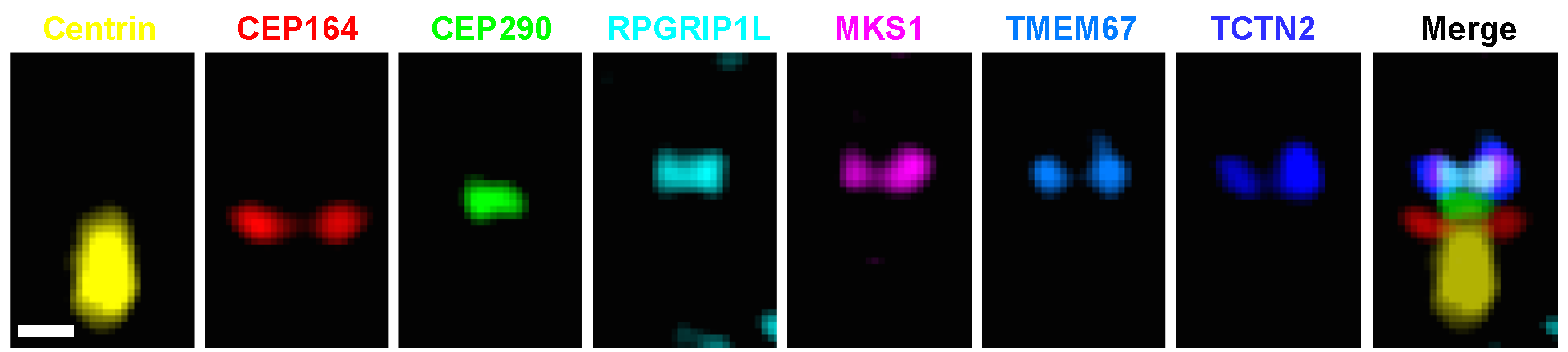
The transition zone (TZ) of primary cilia serves as a diffusion barrier to regulate ciliogenesis and receptor localization for key signaling events such as sonic hedgehog signaling. Its gating mechanism is poorly understood due to the tiny volume accommodating a large number of ciliopathy-associated molecules. Here we performed stimulated emission depletion (STED) imaging of collective samples and recreated superresolved relative localizations of eight representative species of ciliary proteins using position averages and overlapped with representative electron microscopy (EM) images, defining an architectural foundation at the ciliary base. Upon this framework, transmembrane proteins TMEM67 and TCTN2 were accumulated at the same axial level as MKS1 and RPGRIP1L, suggesting that their regulation roles for tissue-specific ciliogenesis occur at a specific level of the TZ. CEP290 is surprisingly localized at a different axial level bridging the basal body (BB) and other TZ proteins. Upon this molecular architecture, two reservoirs of intraflagellar transport (IFT) particles, correlating with phases of ciliary growth, are present: one colocalized with the transition fibers (TFs) while the other situated beyond the distal edge of the TZ. Together, our results reveal an unprecedented structural framework of the TZ, facilitating our understanding in molecular screening and assembly at the ciliary base.
 中央研究院 原子與分子科學研究所
中央研究院 原子與分子科學研究所

