Research Highlights
Dr. Hsiang-Hua Jen
(2025)
Chimdessa Gashu Feyisa, J-S You, Huan-Yu Ku and H H Jen
Quantum Sci. Technol. 10 025021 (2025).
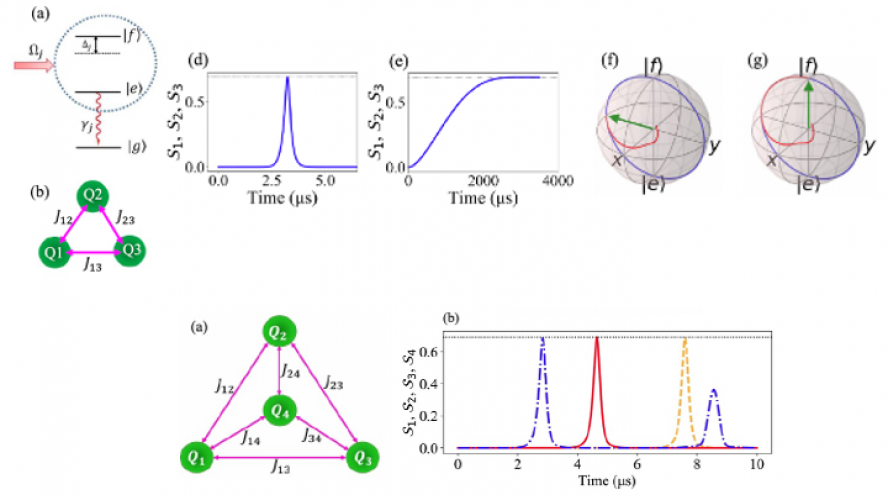
Open quantum systems are susceptible to losses in information, energy, and particles due to their surrounding environment. One novel strategy to mitigate these losses is to transform them into advantages for quantum technologies through tailored non-Hermitian quantum systems. In this work, we theoretically propose a fast generation of multipartite entanglement in non-Hermitian qubits. Our findings reveal that weakly coupled non-Hermitian qubits can accelerate multiparty entanglement generation by thousands of times compared to Hermitian qubits, in particular when approaching the 2^n-th order exceptional points of n qubits in the PT-symmetric regime. Furthermore, we show that Hermitian qubits can generate GHZ states with a high fidelity more than 0.9995 in a timescale comparable to that of non-Hermitian qubits, but at the expense of intense driving and large coupling constant. Our approach is scalable to a large number of qubits, presenting a promising pathway for advancing quantum technologies through the non-Hermiticity and higher-order exceptional points in many-body quantum systems.
Chih-En Shen, Hung-Sheng Tsai, Liang-Yan Hsu*
J. Chem. Phys. 162, 034107 (2025).
![Representative picture of Non-Adiabatic Quantum Electrodynamic Effects on Electron–Nucleus–Photon Systems: Single Photonic Mode vs Infinite Photonic Modes [Feature Article] Representative picture of Non-Adiabatic Quantum Electrodynamic Effects on Electron–Nucleus–Photon Systems: Single Photonic Mode vs Infinite Photonic Modes [Feature Article]](../image/research/org/research-301.jpeg)
The quantum-electrodynamic non-adiabatic emission (QED-NAE) is a type of radiatively assisted vibronic de-excitation due to electromagnetic vacuum fluctuations on non-adiabatic processes. Building on our previous work [Tsai et al., J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14, 5924 (2023)], we extend the theory of the QED-NAE rate from a single cavity photonic mode to infinite photonic modes and calculate the QED-NAE rates of 9-cyanoanthracene at the first-principles level. To avoid the confusion, the quantum electrodynamic internal conversion process is renamed as “QED-NAE” in our present work. According to our theory, we identify three key factors influencing the QED-NAE processes: light–matter coupling strength (mode volume), mass-weighted orientation factor, and photonic density of states. The mode volume is the primary factor causing rate differences between the two scenarios. In a single cavity with a small mode volume, strong light–matter coupling strength boosts QED-NAE rates. In contrast, in free space with infinite photonic modes, weak coupling strength significantly reduces these rates. From a single cavity photonic mode to infinite photonic modes, the mass-weighted orientation factor only causes an 8π/3-fold increase in the QED-NAE rate. In free space, the photonic density of state exhibits a flat and quadratic distribution, which slightly reduces the QED-NAE rate. Our study shows that cavities can significantly enhance non-adiabatic QED effects while providing a robust analysis demonstrating that QED vibronic effects can be safely ignored in free space.
Dr. Chia-Lung Hsieh
(2024)
Nathan J. Brooks, Chih-Chen Liu, Yan-Hsien Chen, and Chia-Lung Hsieh*
ACS Photonics 11(12), 5239–5250 (2024)

Interferometric scattering (iSCAT) microscopy is currently among the most powerful techniques available for achieving high-sensitivity single-particle localization. This capability is realized through homodyne detection, where interference with a reference wave offers the promise of exceptionally precise three-dimensional (3D) localization. However, the practical application of iSCAT to 3D tracking has been hampered by rapid oscillations in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) as particles move along the axial direction. In this study, we introduce a novel strategy based on back pupil plane engineering, wherein a spiral phase mask is used to redistribute the phase of the scattered field of the particle uniformly across phase space, thus ensuring consistent SNR as the particle moves throughout the focal volume. Our findings demonstrate that this modified spiral phase iSCAT exhibits greatly enhanced localizability characteristics. Additionally, the uniform phase distribution enables reliable characterization of the particle’s optical properties regardless of its position. We substantiate our theoretical results with numerical and experimental demonstrations, showcasing the practical application of this approach for high-precision, ultrahigh-speed (20,000 frames per second) 3D tracking and polarizability measurement of freely diffusing nanoparticles as small as 20 nm.
Te-I Liu*, Jhih-Shan Wang, Ai-Phuong Nguyen, Marco Raabe, Carlos Jose Quiroz Reyes, Chih-Hsin Lin, Ching-Wei Lin*
ACS Nano 18, 18534–18547 (2024).

Cytometry plays a crucial role in characterizing cell properties, but its restricted optical window (400-850 nm) limits the number of stained fluorophores that can be detected simultaneously and hampers the study and utilization of short-wave infrared (SWIR; 900-1,700 nm) fluorophores in cells. Here we introduce two SWIR-based methods to address these limitations: SWIR flow cytometry and SWIR image cytometry. We develop a quantification protocol for deducing cellular fluorophore mass. Both systems achieve a limit of detection of ~0.1 fg cell−1 within a 30-min experimental timeframe, using individualized, high-purity (6,5) single-wall carbon nanotubes as a model fluorophore and macrophage-like RAW264.7 as a model cell line. This high-sensitivity feature reveals that low-dose (6,5) serves as an antioxidant, and cell morphology and oxidative stress dose-dependently correlate with (6,5) uptake. Our SWIR cytometry holds immediate applicability for existing SWIR fluorophores and offers a solution to the issue of spectral overlapping in conventional cytometry.
