Direct gas-phase formation of formic acid through reaction of Criegee intermediates with formaldehyde
Pei-Ling Luo*, I-Yun Chen, M. Anwar H. Khan, and Dudley E. Shallcross
Communications Chemistry, 6, 130 (2023)
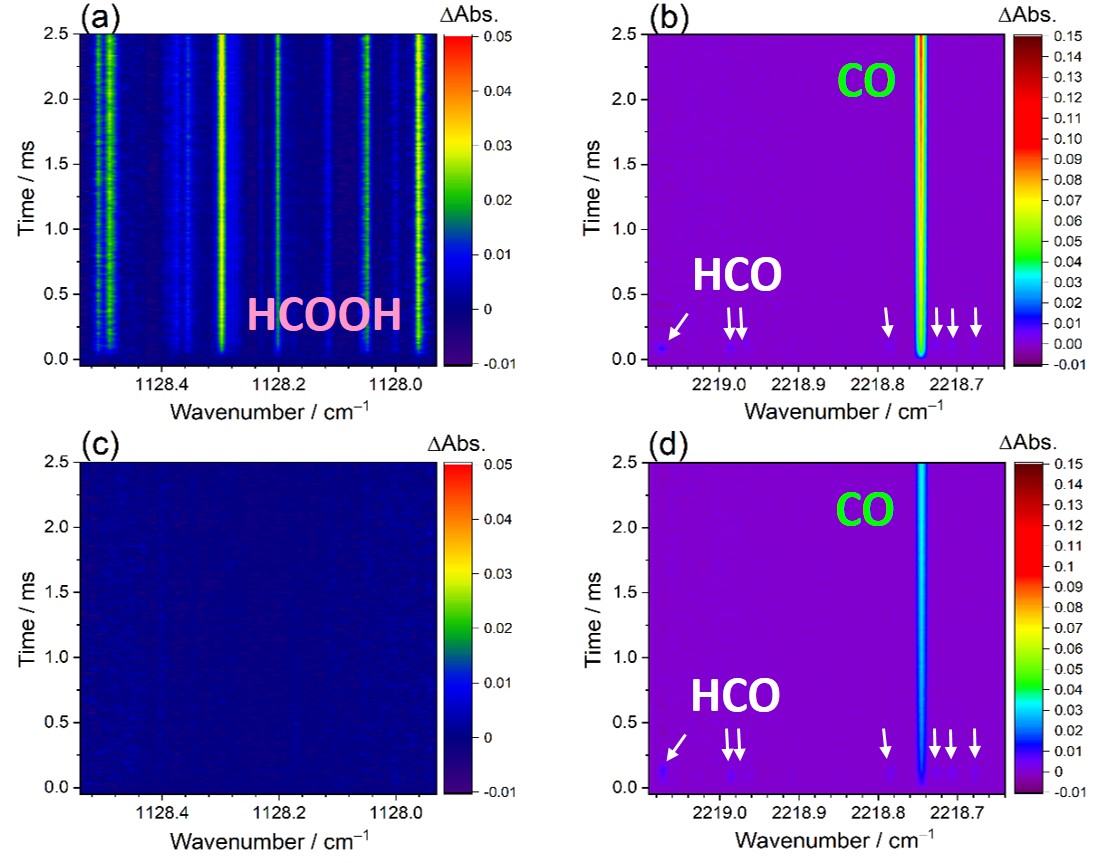
Ozonolysis of isoprene is considered to be an important source of formic acid (HCOOH), but its underlying reaction mechanisms related to HCOOH formation are poorly understood. Here, we report the kinetic and product studies of the reaction between the simplest Criegee intermediate (CH2OO) and formaldehyde (HCHO), both of which are the primary products formed in ozonolysis of isoprene. By utilizing time-resolved infrared laser spectrometry with the multifunctional dual-comb spectrometers, the rate coefficient kCH2OO+HCHO is determined to be (4.11 ± 0.25) × 10−12 cm3 molecule−1 s−1 at 296 K and a negative temperature dependence of the rate coefficient is observed and described by an Arrhenius expression with an activation energy of (–1.81 ± 0.04) kcal mol−1. Moreover, the branching ratios of the reaction products HCOOH + HCHO and CO + H2O + HCHO are explored. The yield of HCOOH is obtained to be 37–54% over the pressure (15–60 Torr) and temperature (283–313 K) ranges. The atmospheric implications of the reaction CH2OO + HCHO are also evaluated by incorporating these results into a global chemistry-transport model. In the upper troposphere, the percent loss of CH2OO by HCHO is found by up to 6% which can subsequently increase HCOOH mixing ratios by up to 2% during December-January-February months.